Software Testing Trends 2019 Recap | Industry Insights

2019 is almost over. The software testing landscape has seen numerous introductions in new testing approaches and innovations at an exponential rate. It has also witnessed the continuation of technological improvement, evolution, and reinvention. As we are progressing to 2020, let’s take a retrospective look at the top trends in test automation and see how we stand after one year.
Our team at Katalon has reflected on the most popular trends that took place in the software testing industry over the course of one year. We have compiled the five most influential software testing trends in 2019. Check them out!
1. Continuous Testing Gets Even More Popular
Continuous testing persisted in going mainstream. Although this concept was coined back in the early 2010s, it was forecast to become trendy in 2019.
Continuous testing is a software testing method that allows a constant flow of feedback between the developers and testers — throughout the entire software development lifecycle. Its value? A faster, more cost-efficient, and less perilous way to reduce bottlenecks among departments. To enable continuous testing, teams must reach an automation rate of 85% or higher — and we expected to witness this phenomenon in 2019.
Moreover, as more and more software organizations embrace the practice of Agile and DevOps, continuous testing is widely adopted. “Quality at Speed” is no longer a new norm in software delivery. Many practices have been introduced and recommended to attain this desired scenario, including continuous testing. Therefore, this method was predicted to have an enormous impact on achieving both the “quality” and “speed” factors of this puzzle.
2. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Quality Assurance
The state of 2019 AI/ML in testing
It was expected in 2019 that there would be more artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) applications in quality assurance such as quality prediction, test case prioritization, defects classification, computer vision, interaction with the application under test, and so on.
Organizations have been scouring for ways to make the best of technological advances so that they can cope with fast-paced releases, frequent changes (see Autohealing SmartXPath), mass operating environments, and everything operates in a state of flux. As a result, more test cases have to be generated, more test scripts have to be written, more test data have to be collected, and more reports have to be evaluated.
With such a vast amount of workload and information to handle, organizations must figure out how to optimize the execution process, process all the data, and provide feedback in not only a fast, but also an accurate fashion.
AI/ML is one of the promising solutions. New algorithms are developed to help users generate better test cases. Predictive modeling is leveraged to help decide where, what, and when to test. Smart analytics and visualization will help teams understand the big picture of their test scenarios and make decisions faster, better.
Challenges and potentials of AI/ML in software testing
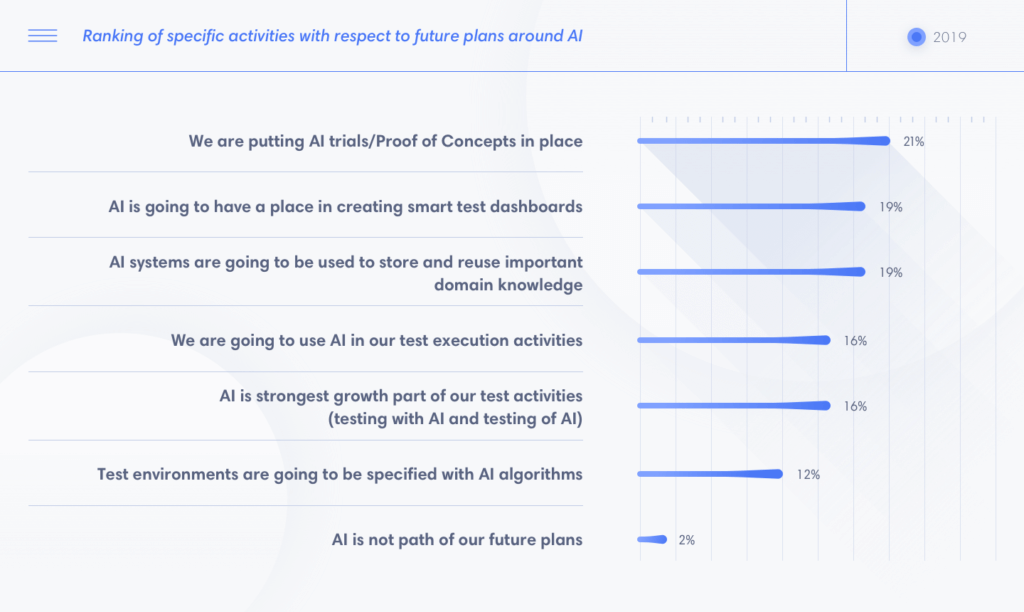
However, the maturity of these technologies is still under development. Budget allocations for AI projects seem to have dropped, compared to 2018 (Capgemini World Quality Report 2019-20). Feedback on AI project commitment also decreased in a lot of scenarios. The assumptions are that organizations are still not confident enough to invest in AI. Furthermore, the maintenance cost may be higher than what organizations desire.
In contrast, adoption levels for ML projects seem promising in 2019, and are used to predict defects and prioritizing which test cases to use. Huge collections of data need to be gathered, the ML mechanisms need to prove that they work — but the anticipation for this technology is, no doubt, growing.

We’ve been surrounded by a world of AI/ML. These two notions are widely applied to a majority of aspects — including software testing.
Although these concepts are no longer new, the increasing abundance of available data and technological advancements opens up more opportunities for AI and ML in testing.
3. Intelligent Automation
The next item in this software testing trends list is about applying intelligent automation frameworks, tools, and techniques.
In early 2019, it was speculated that more organizations would continue to apply automation to software testing projects.
This is mainly due to the shift toward Agile and DevOps. The increasingly high demand for Quality at Speed requires teams to automate the mundane activities, so that they can focus on strategic planning and evaluating decisions.
Automation — if applied properly — will allow software development teams to increase test coverage, improve test efficiency, receive faster feedback, reuse test cases, detect bugs early, and more. As a result, teams can ensure a higher quality of the delivered software.
About 44% of organizations expect to automate 50% or more of all testing in 2019, according to a study on test automation trends. Teams that reach this level of test automation see numerous benefits.
Promising adoption rates of test automation
The adoption rate of automation saw progress in 2018, and was expected to escalate in 2019. This has been shown to be true.
Research shows that organizations were positive about the benefits accrued from automation in 2019. More teams have realized the benefits of applying automation to their SDLC, including better control of test activities, more transparency, and more accurate detection of defects. They also reported that automation helped them reduce unpleasant outcomes, such as test costs, test cycle time, and overall security risk.

Challenges with test automation
The other side of the coin is the challenges faced by organizations while adopting automation.
Almost two-thirds of the respondents in a study found it difficult to automate because their applications change too much with each release. Lack of skills and appropriate resources are also major obstacles of automation.

What’s next for software test automation?
Moving forward, the concept of test automation has been popularized for about 20 years now. However, many dilemmas are still in the picture.
A key reason why teams have not been able to achieve their desired outcomes of automation is because most automation frameworks were designed to automate only manual tasks. We need an automation framework that:
- significantly reduces the programming effort, especially for teams that do not have much programming expertise see Katalon Manual View
- intelligently decides when to perform certain tasks such as execution, without human interference see Katalon Smart Wait
- is dynamic enough, such as using cognitive computing techniques to identify test objects and screen elements effectively
- prioritizes, identifies, and executes the critical test cases from the automated suite
- provides its own test data
4. Test Data and IoT Testing
The continuous expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT) has immersed over the past years. According to Gartner, by 2020, the number of IoT devices all over the world will reach 20.4 billion. More IoT devices means more online connection and data exposure — which means, more risks.
In 2019, IoT was expected to be conducted in testing. IoT testing is the technique of checking IoT devices. These types of testing include:
- Usability testing: tests the usability of IoT systems
- Performance testing: tests the performance of the connected devices in an IoT network
- Compatibility testing: checks the compatibility of devices in IoT systems
- Security testing: validates user authentication processes and data privacy controls
- Data integrity testing: validates data integrity
- Reliability and Scalability testing: sensors simulation using virtualization tools
The rise of IoT systems is closely connected to the growth of applications of AI/ML to help generate test data and data projects. The automation industry also expects to see an increase in usage of cloud-based and containerized test environments, and solutions for the lack of test data.
It is suggested that QA teams need to step up their game if they want to ensure security in IoT systems. Three critical steps that they need to take on include: applying continuous security testing, being strategic on what needs and does not need to be tested to be operationally efficient, and implementing service virtualization as part or their automation strategies.
5. Behavior-Driven Development Reaches New Maturity Stage

The final item of the latest trends in software testing is about behavior-driven development (BDD).
As mentioned in the 12th Annual State of Agile report, only 16% of organizations apply BDD methodologies in 2018 — but this number was forecast to increase in the next year.
A byproduct of increasing test automation is the growing maturity of BDD. As a matter of fact, more teams were expected to flow through the BDD maturity model. This model includes five stages:
- Embrace BDD collaboration
- Implement BDD tools and frameworks
- Connect systems for development and automation
- Standardize continuous integration and systemic collaboration
- Report on BDD success
Conclusion
We hope this recap has played a part in giving better insights on the software testing trends of 2019 — so that organizations can reflect to reinforce their strategies. These trends are among the latest trends in the software testing big picture. The quality assurance landscape will continue to evolve. We’re excited to see what’s going to change and what’s going to be introduced in the next year.
Among these trends, which one has worked for your organization? Which is your favorite? Share your thoughts with us.
Comments
Post a Comment